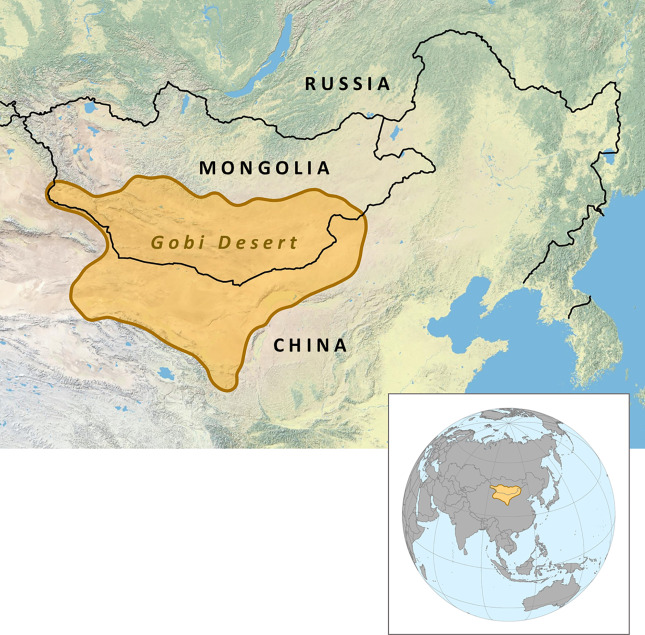
Discover the Mysteries of the Gobi Desert and Gobi Region Mongolia
Exploring the vast expanse of the Gobi Desert-Iran Charter offers a unique opportunity to understand one of the most intriguing landscapes in the world. The Gobi Desert-Iran Charter spans a significant part of the Gobi Region Mongolia, renowned for its breathtaking natural beauty, rich history, and diverse wildlife. This region, characterized by its expansive deserts, rugged mountains, and resilient flora and fauna, has captivated explorers and scientists alike for centuries. The Gobi Desert-Iran Charter is not just a desert; it is a living testament to Earth’s geological and ecological processes, offering insights into climate change, ancient civilizations, and ongoing conservation efforts. Visitors and researchers who venture into this area are rewarded with spectacular landscapes, fossil discoveries, and a glimpse into the resilience of life in extreme environments. Understanding the Gobi Desert-Iran Charter helps us appreciate the delicate balance of natural ecosystems and the importance of sustainable tourism and environmental protection in this extraordinary region. The Gobi Desert-Iran Charter continues to be a focal point for scientific research, adventure tourism, and cultural exploration, making it a must-visit destination for those seeking to connect with nature’s raw beauty and ancient history.
Discover the Rich History and Mysteries of the Gobi Desert in Mongolia
The Gobi Desert in Mongolia is a region steeped in ancient history and filled with countless secrets waiting to be uncovered. This vast landscape has been a crossroads of civilizations for thousands of years, serving as a vital route for trade caravans and a home to diverse cultures. Archaeological excavations reveal that humans have inhabited the Gobi since prehistoric times, leaving behind artifacts that tell stories of early settlements, ancient trade routes, and cultural exchanges. The mysteries of the Gobi continue to intrigue researchers and explorers alike, as new discoveries shed light on its significance in human history. From ancient fossils to relics of bygone eras, the Gobi Desert holds the key to understanding the development of civilizations in Central Asia. Ongoing archaeological projects aim to decode these secrets, offering insights into the region’s past and its role in shaping the history of Mongolia and beyond. Exploring the history of the Gobi provides a deeper appreciation of its importance as a cradle of ancient cultures and a witness to the passage of time. Its historical significance makes it a must-visit destination for history enthusiasts and adventurers seeking to connect with the ancient world. The mysteries of the Gobi continue to inspire scientific research, promising more revelations about this enigmatic landscape. Understanding its past helps preserve its heritage and promotes sustainable tourism that respects its archaeological treasures.
The Unique Geography of the Gobi: A Land Unlike Any Other in Central Asia
The Gobi Desert spans a vast and diverse area in the heart of Central Asia, covering parts of Mongolia and China. Its distinctive geography features a mix of expansive plains, rugged mountains, and deep valleys, creating a landscape that is both dramatic and varied. The terrain is characterized by rocky outcrops, sand dunes, and sparse vegetation, reflecting its arid climate and harsh environmental conditions. Despite the extreme dryness, some regions of the Gobi support hardy plant life and serve as habitats for unique wildlife adapted to desert life. The mountain ranges, such as the Altai, provide a striking contrast to the flat desert plains, offering breathtaking vistas and diverse ecosystems. The region’s geographical features influence its climate, with cold winters, hot summers, and strong winds shaping its environment. The Gobi’s topography has historically served as both a barrier and a corridor for migration and trade, shaping the cultural and ecological landscape. Its geological formations contain valuable mineral deposits, making it an important area for resource exploration. Preserving the unique geography of the Gobi is essential for maintaining its ecological balance and supporting sustainable development. The region’s diverse landscape continues to attract scientists, travelers, and conservationists eager to explore its natural wonders.
Environmental Conservation and Challenges in the Gobi Desert
Efforts to protect the fragile ecosystem of the Gobi Desert are vital for maintaining its biodiversity and preventing further desertification. Various environmental projects focus on combating the expansion of the desert, restoring native vegetation, and managing water resources sustainably. Initiatives such as afforestation, controlled grazing, and water conservation aim to stabilize the landscape and support local communities. However, the Gobi faces significant challenges, including climate change, overgrazing, and illegal resource extraction, which threaten its ecological stability. Rising temperatures and irregular rainfall patterns accelerate desertification, impacting both wildlife and human livelihoods. Addressing these issues requires coordinated efforts among governments, NGOs, and local populations to implement sustainable practices. Successful conservation projects have seen the reintroduction of native plant species, increased awareness about environmental protection, and the establishment of protected areas. These measures help preserve the unique flora and fauna of the region, including rare species like the Gobi bear and snow leopards. Promoting eco-tourism and environmental education also play crucial roles in fostering sustainable development. Protecting the Gobi’s environment ensures that future generations can enjoy its natural beauty and ecological richness. Continued research and adaptive management are essential to overcoming ongoing challenges and securing a sustainable future for this iconic desert.
The Marvels of Nature and Unique Fauna of the Gobi
The Gobi Desert is home to some of the most extraordinary natural phenomena and rare animal species. Fossil discoveries of dinosaurs and ancient marine life highlight the region’s rich prehistoric past and scientific importance. These fossils provide valuable insights into Earth’s history and the evolution of life. The desert’s extreme environment has fostered the development of resilient species such as the Bactrian camel, which is perfectly adapted to survive in harsh conditions. Other remarkable animals include the elusive Gobi bear, one of the rarest bears in the world, and the graceful snow leopards that roam the mountainous areas. Birdwatchers can spot rare species like the black vulture and various migratory birds that visit the region seasonally. The diverse landscape, from sand dunes to rocky outcrops, supports a wide range of flora and fauna uniquely suited to desert life. These natural wonders not only attract scientists and eco-tourists but also emphasize the importance of conserving this fragile ecosystem. Protecting these species ensures the preservation of the Gobi’s natural heritage and promotes biodiversity. The region’s natural marvels continue to inspire awe and curiosity, offering a glimpse into Earth’s ancient and resilient ecosystems.
Impact of Climate Change and Human Activities on the Gobi’s Expansion
The ongoing expansion of the Gobi Desert is closely linked to climate change and human activities. Rising temperatures and decreasing precipitation accelerate desertification, reducing arable land and water availability. Overgrazing by livestock and deforestation for fuel and construction further degrade the environment, leading to loss of vegetation cover and soil erosion. These factors create a vicious cycle, where environmental degradation worsens due to climate variability, threatening local livelihoods and biodiversity. Addressing these issues requires integrated strategies that include sustainable land management, reforestation, and water conservation. Community involvement and education are crucial for implementing effective practices that mitigate human impact. International cooperation and policy support can enhance resilience against climate change effects. Innovative solutions such as drought-resistant crops and water-saving technologies are being adopted to adapt to changing conditions. Protecting the Gobi from further expansion demands a balance between development and conservation, ensuring the region remains sustainable for future generations. Recognizing the importance of climate resilience is essential to preserving the ecological and cultural integrity of this unique desert landscape.
Historical Trade Routes and the Role of the Gobi in Eurasian Commerce
The Gobi Desert has historically served as a vital corridor for trade and cultural exchange across Eurasia. The famous Silk Road traversed parts of this region, connecting China with Central Asia, the Middle East, and Europe. Caravans crossing the Gobi facilitated the exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies, fostering economic and cultural development. These routes contributed to the spread of Buddhism, art, and scientific knowledge, shaping civilizations along the way. Today, the region continues to hold strategic importance as modern trade routes develop, linking China with Mongolia and neighboring countries. The historical significance of the Gobi as a trade hub underscores its role in shaping regional history and geopolitics. Preserving the legacy of these ancient routes offers opportunities for cultural tourism and educational initiatives. Modern infrastructure projects aim to revitalize trade corridors, boosting economic growth while respecting the region’s heritage. Understanding the Gobi’s role in Eurasian commerce highlights its enduring importance as a bridge between East and West. Promoting sustainable development along these routes can foster economic prosperity while safeguarding cultural and historical assets.
Innovative Ecotourism and Sustainable Travel in the Gobi
Ecotourism in the Gobi Desert offers travelers a chance to experience its natural beauty responsibly and sustainably. Tours focus on low-impact activities such as guided desert walks, wildlife observation, and cultural immersion with local nomadic communities. These experiences promote environmental awareness and support local economies through responsible tourism practices. Many eco-lodges and camps are designed to blend seamlessly into the landscape, utilizing renewable energy sources and water-saving technologies. Visitors can participate in traditional nomadic activities, learn about indigenous customs, and enjoy authentic local cuisine. Promoting eco-friendly travel helps preserve the region’s fragile ecosystems and cultural heritage for future generations. Educational programs and community involvement are key components of sustainable tourism initiatives, ensuring that tourism benefits local populations and minimizes environmental impact. The Gobi’s vast, untouched landscapes provide a perfect setting for eco-conscious travelers seeking adventure and cultural exchange. Developing responsible tourism strategies can turn the Gobi into a global model for sustainable travel, balancing economic growth with ecological preservation. This approach ensures that the natural and cultural treasures of the Gobi remain intact and accessible for generations to come.
Ancient Art and Archaeological Discoveries in the Heart of the Gobi
The Gobi Desert is a treasure trove of ancient art and archaeological sites that reveal the rich cultural history of the region. Excavations have uncovered intricate petroglyphs, ancient burial sites, and relics from early civilizations that inhabited this harsh landscape. These artifacts depict scenes of hunting, spiritual rituals, and daily life, offering a window into the past. The region’s archaeological significance is heightened by discoveries of dinosaur fossils, some dating back over 70 million years, making it a world-renowned paleontological site. Preservation of these sites is crucial for understanding human history and prehistoric life. Ongoing research aims to uncover more hidden stories buried beneath the sands, shedding light on migration patterns, cultural exchanges, and technological advancements. Educational programs and tourism initiatives help raise awareness about the importance of protecting these invaluable cultural assets. The art and relics of the Gobi continue to inspire scholars, artists, and visitors, emphasizing the region’s role as a cradle of ancient civilizations. Protecting these archaeological treasures ensures that the stories of the past remain alive for future generations to learn from and appreciate.
Traditional Nomadic Life and Cultural Heritage of the Gobi People
The nomadic communities of the Gobi Desert have preserved their unique lifestyle, customs, and traditions despite modern challenges. Their way of life revolves around livestock herding, seasonal migrations, and a deep connection to the land. Traditional practices such as herding camels, sheep, and goats are passed down through generations, maintaining a sustainable relationship with the environment. Cultural expressions like music, dance, and craftsmanship reflect the rich heritage of the Gobi nomads. Their yurts (gers), clothing, and oral storytelling are vital components of their identity, embodying resilience and adaptability. However, economic pressures, climate change, and modernization pose threats to their traditional way of life. Efforts to support nomadic communities include promoting eco-tourism, providing access to education, and developing sustainable livelihoods. Preserving their cultural heritage fosters a sense of pride and continuity, ensuring that future generations can carry forward these ancient traditions. Engaging with local communities enhances cultural understanding and promotes responsible tourism that respects their way of life. The nomadic spirit of the Gobi remains a testament to human resilience and harmony with nature, offering valuable lessons for sustainable living.
Frequently Asked Questions about the Gobi Desert in Mongolia
- What is the historical significance of the Gobi Desert?
- The Gobi Desert has been a vital crossroads for civilizations for thousands of years. Archaeological excavations reveal early human settlements, ancient trade routes like the Silk Road, and relics that tell stories of cultural exchanges and technological advancements. Its fossils and artifacts provide insights into prehistoric life and the development of civilizations in Central Asia.
- How does the geography of the Gobi Desert differ from other deserts?
- The Gobi spans a vast area with a mix of plains, rugged mountains, and deep valleys. Its terrain includes rocky outcrops, sand dunes, and sparse vegetation, shaped by an arid climate. The Altai mountain range and other geological features create a diverse landscape that influences local climate and ecosystems.
- What are the main environmental challenges facing the Gobi?
- The region faces desertification due to climate change, overgrazing, and illegal resource extraction. Rising temperatures and irregular rainfall accelerate environmental degradation, threatening biodiversity and local livelihoods. Conservation efforts focus on reforestation, water management, and sustainable land use.
- What unique wildlife can be found in the Gobi Desert?
- The Gobi hosts remarkable species such as the Bactrian camel, the rare Gobi bear, snow leopards, and migratory birds. Fossil discoveries of dinosaurs also highlight its prehistoric significance. Protecting these species is vital for maintaining the region’s ecological balance.
- How is climate change impacting the Gobi’s expansion?
- Climate change causes rising temperatures and decreased rainfall, which intensify desertification. Overgrazing and deforestation further degrade the environment, creating a cycle of land loss and ecological imbalance that threatens both wildlife and local communities.
- What role did the Gobi play in ancient trade routes?
- The Gobi was a key part of the Silk Road, facilitating trade and cultural exchange between China, Central Asia, and beyond. Caravans crossing the desert spread goods, ideas, and religions, shaping civilizations along the route. Today, it remains a strategic corridor for modern trade development.
- What are some sustainable tourism practices in the Gobi?
- Eco-tourism in the Gobi emphasizes low-impact activities like guided desert walks, wildlife observation, and cultural experiences with nomadic communities. Eco-lodges with renewable energy and water conservation technologies help preserve the environment while supporting local economies.
- What archaeological discoveries have been made in the Gobi?
- The region is rich in ancient art, petroglyphs, and dinosaur fossils dating back over 70 million years. These findings shed light on prehistoric life and early human cultures. Preservation and ongoing research are crucial to uncover more secrets buried beneath the sands.
- How do the nomadic communities sustain their traditional lifestyle?
- Nomads herd livestock such as camels, sheep, and goats, migrating seasonally to find pasture. Their customs include music, dance, and craftsmanship, which are passed down through generations. Support initiatives focus on eco-tourism, education, and sustainable livelihoods to preserve their heritage.
- What makes the Gobi a natural wonder?
- The Gobi’s diverse landscapes, fossils, rare wildlife, and geological formations make it a unique natural wonder. Its extreme environment fosters resilient species and offers scientific insights into Earth’s prehistoric past, attracting researchers and eco-tourists alike.
- What are the main conservation efforts in the Gobi?
- Projects include afforestation, water management, and protected areas to combat desertification and protect biodiversity. International and local initiatives aim to restore native vegetation, reintroduce endangered species, and promote eco-friendly development.
- How does the Gobi Desert influence regional climate?
- The Gobi’s topography and arid climate influence local weather patterns, with cold winters, hot summers, and strong winds. Its environment impacts surrounding regions, contributing to climate variability and ecological dynamics across Central Asia.
- What are the benefits of eco-tourism in the Gobi?
- Eco-tourism promotes environmental awareness, supports local communities, and helps preserve the region’s natural and cultural heritage. Responsible travel minimizes ecological impact and provides economic opportunities for nomadic populations.
- What role do fossils play in understanding the Gobi’s past?
- Fossil discoveries, especially of dinosaurs, reveal the region’s prehistoric ecosystems and evolutionary history. These findings attract scientists worldwide and contribute to global knowledge about Earth’s ancient past.
- How do the ancient trade routes impact Mongolia today?
- The historic trade routes laid the foundation for modern infrastructure and economic development. They foster cultural connections and tourism, highlighting the Gobi’s ongoing strategic importance in regional commerce.
























