Discover the Wonders of Lake Tanganyika in the Kigoma Region of Tanzania
Lake Tanganyika, located in the Kigoma Region of Tanzania, stands as one of the most remarkable natural wonders in Africa. This expansive freshwater lake, renowned for its breathtaking scenery and rich biodiversity, attracts travelers, researchers, and nature enthusiasts from around the world. Covering an area of over 32,900 square kilometers, Lake Tanganyika is not only the longest freshwater lake in the world but also the second deepest, reaching depths of more than 1,470 meters. Its unique ecological environment supports thousands of aquatic species, many of which are endemic and found nowhere else on Earth. The lake’s crystal-clear waters, surrounded by lush green landscapes and rugged mountains, create a mesmerizing backdrop that offers unparalleled opportunities for eco-tourism, fishing, and cultural exploration. Visiting Lake Tanganyika in the Kigoma Region provides an immersive experience into the natural beauty and diverse ecosystems that define this extraordinary part of Tanzania. Whether you’re interested in exploring vibrant local communities, engaging in water sports, or simply relaxing amidst pristine nature, Lake Tanganyika offers an unforgettable adventure that highlights the ecological and cultural richness of the Kigoma Region in Tanzania.
For more information about exploring this magnificent lake and its surroundings, visit Lake Tanganyika-Iran Charter.
Discover the beauty of Lake Tanganyika in the Kigoma Region of Tanzania and experience a journey into one of Africa’s most captivating natural landscapes. From its diverse aquatic life to its scenic vistas, this lake is a treasure trove for nature lovers and adventure seekers alike. Plan your visit today and immerse yourself in the wonders of this unique ecosystem, which continues to inspire conservation efforts and sustainable tourism initiatives in the region.

Discover the Rich History and Formation of Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region Tanzania
Lake Tanganyika, situated in the Kigoma Region of Tanzania, is one of the world’s oldest and deepest freshwater lakes, with a history dating back millions of years. Its formation is a result of complex geological processes involving tectonic activity in the East African Rift Valley. Over the millennia, this ancient lake has played a vital role in shaping the environmental and cultural landscape of the region. Understanding its geological history helps appreciate its significance as a natural wonder and ecological treasure.
Throughout its extensive history, Lake Tanganyika has experienced fluctuations in water levels and structural changes, leading to a diverse array of habitats and species. Its age and stability have contributed to the evolution of unique aquatic life forms that are found nowhere else on Earth. Recognizing the lake’s historical development is crucial for effective conservation and sustainable management efforts in the Kigoma Region.
Studying the formation and evolution of Lake Tanganyika provides insights into regional climate patterns, geological shifts, and environmental changes over millions of years. Preserving this historic lake is essential for maintaining biodiversity, supporting local communities, and safeguarding a natural heritage that has persisted through ages.
Unique Biodiversity and Endemic Species of Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region Tanzania
Lake Tanganyika is renowned for its extraordinary biodiversity, hosting over 250 endemic fish species, many of which are found exclusively within its waters. The lake’s long history and stable environment have fostered an evolutionary hotspot, leading to the development of highly specialized aquatic species. These include various cichlids, catfish, and unique invertebrates that contribute to the lake’s ecological richness.
Among the most notable are the diverse cichlid fish, which exhibit remarkable adaptations to different ecological niches within the lake. These species are vital for maintaining ecological balance and are of significant scientific interest due to their evolutionary processes. The lake also supports rare crustaceans and mollusks that thrive in its unique conditions.
Protecting this biodiversity is critical, as many species face threats from overfishing, habitat degradation, and pollution. Conservation initiatives aim to preserve these endemic species, ensuring the ecological integrity of Lake Tanganyika and its importance as a natural laboratory for biological research.
Economic Significance of Lake Tanganyika for Kigoma Region Tanzania
Lake Tanganyika is a cornerstone of the local economy in the Kigoma Region, providing vital resources such as fish for food security and livelihoods. The lake’s abundant fish populations support commercial and subsistence fishing, which sustains thousands of families and contributes significantly to regional income.
Beyond fishing, the lake supports industries like fish processing, boat transportation, and tourism. The export of fish products generates foreign exchange, while ecotourism related to the lake’s scenic beauty and wildlife attracts visitors, creating employment opportunities. Sustainable management of these resources is essential for long-term economic development.
Efforts to promote responsible fishing practices, develop infrastructure, and diversify tourism are key strategies to maximize the economic benefits of Lake Tanganyika while ensuring environmental conservation and community well-being.
Stunning Natural Landscapes and Tourist Attractions Around Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region Tanzania
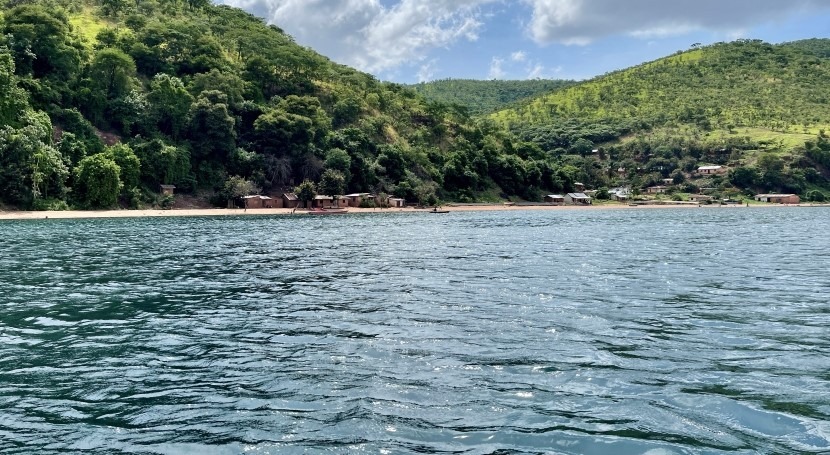
The region surrounding Lake Tanganyika boasts breathtaking landscapes, including lush forests, rugged mountains, and pristine beaches. These natural features create a picturesque setting that attracts nature lovers, adventure seekers, and photographers alike. The scenic views of sunrise and sunset over the lake are truly mesmerizing and offer unforgettable experiences.
Visitors can explore the diverse ecosystems, including national parks and protected areas that harbor rare wildlife and plant species. Activities such as hiking, birdwatching, and boat safaris allow tourists to immerse themselves in the region’s natural beauty. Preserving these landscapes is vital for maintaining the area’s ecological and aesthetic value.
Tourism development in the Kigoma Region emphasizes eco-friendly practices, community involvement, and sustainable use of natural resources, ensuring that future generations can enjoy these natural wonders.
Historical Challenges and Conservation Efforts for Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region Tanzania
Over the years, Lake Tanganyika has faced numerous environmental challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction. Human activities such as unregulated fishing, deforestation, and agricultural runoff have threatened the lake’s ecological health and biodiversity.
In response, various conservation programs have been implemented to protect the lake’s natural resources. These include establishing protected areas, enforcing fishing regulations, and raising awareness among local communities about sustainable practices. Collaborative efforts aim to restore and maintain the ecological balance of Lake Tanganyika.
Continued commitment from government agencies, NGOs, and local stakeholders is essential to address ongoing threats and ensure the lake’s resilience for future generations. Protecting this vital ecosystem is a shared responsibility that benefits both the environment and local livelihoods.
Impact of Climate Change on Lake Tanganyika’s Ecosystem and Communities in Kigoma Region Tanzania
Climate change has begun to affect Lake Tanganyika through rising temperatures, altered rainfall patterns, and increased evaporation rates. These changes lead to fluctuations in water levels, affecting aquatic habitats and fish populations critical for local communities.
Warmer waters can cause shifts in species distribution and reduce biodiversity, while decreased water levels threaten fishing activities and water availability for communities. These environmental shifts also impact agriculture, health, and overall livelihoods in the region.
Adaptive strategies such as improved water management, climate-resilient fishing practices, and community education are vital to mitigate these impacts. Strengthening resilience against climate change is essential to preserve the ecological and economic stability of the Kigoma Region.
Exploring the Depths: Underwater Wonders and Secrets of Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region Tanzania
Lake Tanganyika’s impressive depth and clarity reveal a fascinating underwater world filled with unique habitats and species. The lake’s depths are home to mysterious ecosystems, including rare fish, submerged rock formations, and ancient sediments that tell stories of geological history.
Diving and snorkeling expeditions offer glimpses into this vibrant underwater landscape, showcasing colorful fish, endemic species, and intriguing geological features. These explorations help scientists understand the lake’s ecological dynamics and geological past.
Protecting these underwater treasures requires strict conservation measures, pollution control, and sustainable tourism practices. Unlocking the secrets beneath the surface can contribute to scientific knowledge and promote eco-tourism in the Kigoma Region.
Cultural Heritage and Local Traditions Linked to Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region Tanzania
The communities around Lake Tanganyika have developed rich cultural traditions and stories intertwined with the lake’s presence. Local folklore, rituals, and festivals reflect a deep respect and spiritual connection to this vital water body.
Many tribes consider the lake sacred, and their livelihoods, customs, and identities are closely linked to its resources. Traditional fishing techniques, craft-making, and storytelling preserve the region’s cultural heritage and foster community cohesion.
Efforts to document and promote these cultural practices help sustain the region’s identity while encouraging responsible tourism that respects local traditions. Preserving this intangible heritage is key to maintaining the social fabric of the Kigoma communities.
Recreational Activities and Water Sports on Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region Tanzania
The pristine waters of Lake Tanganyika provide an ideal setting for various recreational activities, including kayaking, sailing, and fishing. These water sports attract both local residents and tourists seeking adventure and relaxation amidst natural beauty.
Engaging in these activities promotes healthy lifestyles and supports local businesses through equipment rentals, guided tours, and hospitality services. Developing sustainable infrastructure ensures safety and environmental protection.
Encouraging eco-friendly water sports and responsible tourism practices helps preserve the lake’s pristine condition while offering memorable experiences for visitors and boosting regional economic growth.

Frequently Asked Questions about Lake Tanganyika in Kigoma Region, Tanzania
- What is the geological history of Lake Tanganyika?
- Lake Tanganyika is one of the world’s oldest and deepest freshwater lakes, formed through complex tectonic processes in the East African Rift Valley. Its formation dates back millions of years, shaped by geological activity that created a stable environment for diverse ecosystems to develop over time.
- How does Lake Tanganyika’s formation influence its biodiversity?
- The ancient and stable geological history of Lake Tanganyika has fostered the evolution of numerous endemic species. Its long-standing existence provides unique habitats that support over 250 fish species found nowhere else on Earth, making it a hotspot for biodiversity.
- What are some endemic species found in Lake Tanganyika?
- The lake hosts a variety of endemic species, especially cichlid fish, which have adapted to different ecological niches. It also supports unique crustaceans and mollusks that contribute to its ecological richness.
- Why is Lake Tanganyika economically important for Kigoma?
- The lake provides vital resources such as fish for local consumption and export, supporting thousands of livelihoods. It also boosts industries like tourism, transportation, and fish processing, playing a key role in regional development.
- What are the main tourist attractions around Lake Tanganyika?
- The region features stunning landscapes, including beaches, forests, and mountains. Visitors enjoy activities like boat safaris, hiking, birdwatching, and exploring national parks, all set against the picturesque backdrop of the lake.
- What challenges has Lake Tanganyika faced historically?
- Environmental issues such as pollution, overfishing, and habitat destruction have threatened the lake’s health. Human activities like unregulated fishing and deforestation have contributed to ecological degradation.
- What conservation efforts are in place for Lake Tanganyika?
- Various initiatives include establishing protected areas, enforcing fishing regulations, and raising awareness among local communities. Collaborative efforts aim to restore ecological balance and ensure sustainable use of resources.
- How is climate change impacting Lake Tanganyika?
- Rising temperatures and altered rainfall patterns are causing fluctuations in water levels, affecting habitats and fish populations. These changes threaten biodiversity and the livelihoods of local communities dependent on the lake.
- What are the underwater features of Lake Tanganyika?
- The lake’s depths reveal unique geological formations, submerged ecosystems, and ancient sediments. These features attract scientists and divers interested in exploring its mysterious underwater world.
- How do local communities relate culturally to Lake Tanganyika?
- Many tribes consider the lake sacred and have cultural traditions linked to it, including rituals, folklore, and festivals. Their livelihoods and identities are deeply connected to the lake’s resources.
- What recreational activities are popular on Lake Tanganyika?
- Water sports like kayaking, sailing, and fishing are common. The pristine waters attract tourists seeking adventure, relaxation, and eco-tourism experiences, supporting local businesses.
- What are the environmental threats facing Lake Tanganyika today?
- Pollution, illegal fishing, habitat destruction, and climate change pose significant risks. These threats require ongoing conservation efforts to protect the lake’s ecological integrity.
- How can visitors help in conserving Lake Tanganyika?
- Tourists can support eco-friendly practices, avoid pollution, and participate in community-based conservation programs. Promoting responsible tourism ensures the lake’s sustainability for future generations.
- What role does Lake Tanganyika play in regional climate studies?
- The lake’s historical water level fluctuations and ecological changes provide valuable data for understanding regional climate patterns and environmental shifts over millions of years.
- What are the future prospects for Lake Tanganyika’s conservation?
- With increased awareness, sustainable management practices, and community involvement, the lake’s ecological health can be preserved. Continued research and international cooperation are essential for its long-term protection.