Discover the Wonders of Manu National Park Madre de Dios Peru: An Unparalleled Biodiversity Haven
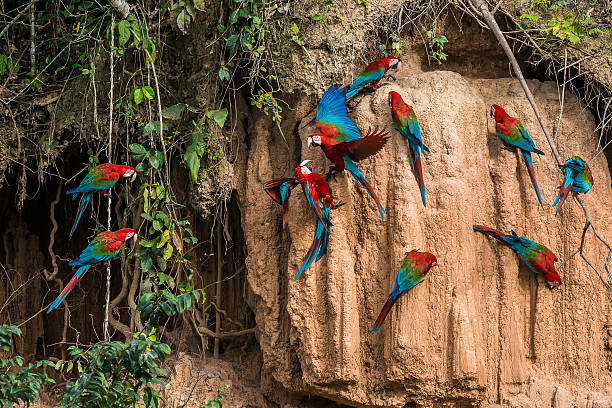
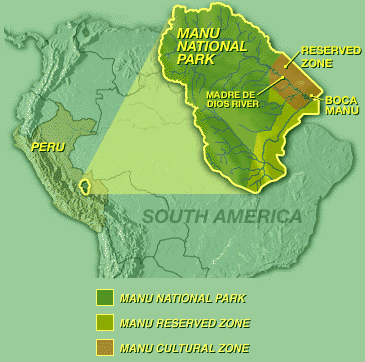
Manu National Park Madre de Dios Peru stands as one of the most remarkable protected areas in South America, renowned for its extraordinary biodiversity and pristine ecosystems. Covering over 1.7 million hectares, this vast wilderness encompasses lush rainforests, towering mountain ranges, and expansive wetlands, making it a vital sanctuary for countless plant and animal species. Visitors to Manu National Park Madre de Dios Peru can witness rare wildlife such as jaguars, giant otters, and hundreds of bird species, many of which are endemic or critically endangered. The park’s diverse habitats support a complex web of life, offering unparalleled opportunities for ecological research and eco-tourism. Exploring Manu National Park Madre de Dios Peru not only provides a glimpse into the richness of tropical ecosystems but also highlights the importance of conservation efforts in safeguarding our planet’s natural heritage. Whether you’re an adventure seeker, a nature lover, or a researcher, this protected area is a must-visit destination to experience the vibrant and fragile beauty of Madre de Dios’s wilderness. Learn more about this extraordinary region and plan your journey to discover the secrets of Manu National Park Madre de Dios Peru today.
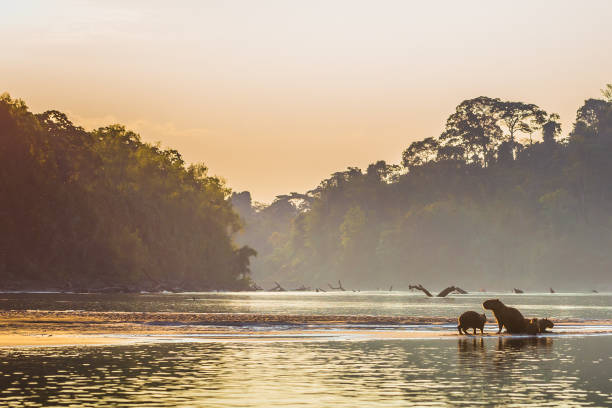

Discover the Unique Biodiversity of Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru
Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, stands as one of the most vital protected areas in South America, renowned for its extraordinary biodiversity. Covering over 1.7 million hectares, this UNESCO World Heritage site encompasses lush rainforests, mountain forests, and high-altitude grasslands. Its diverse habitats are home to rare and endemic species, making it a top destination for ecologists and nature enthusiasts alike. Visitors can experience a rich tapestry of flora and fauna, including jaguars, giant otters, and hundreds of bird species, all contributing to the park’s ecological significance. The park’s vast wilderness plays a crucial role in global conservation efforts, supporting scientific research and environmental sustainability. Exploring Manu offers an unparalleled opportunity to witness nature’s resilience and the importance of preserving such ecological treasures for future generations.
The History and Conservation Milestones of Manu National Park in Madre de Dios
Established in 1973, Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, was among the first protected areas in the country, aimed at conserving its unique ecosystems. Over the decades, it has expanded through strategic boundary adjustments and conservation programs, solidifying its status as a critical biodiversity hotspot. In 1987, UNESCO designated it as a World Heritage Site, recognizing its global ecological importance. The park’s management has evolved with the implementation of sustainable practices, community involvement, and international collaborations. These efforts have helped maintain its pristine condition despite increasing pressures from nearby development. Continuous research and conservation initiatives ensure the park remains a sanctuary for endangered species and a living laboratory for ecological studies. Its history reflects a commitment to safeguarding natural heritage amid changing environmental challenges.
Exciting Tourist Routes and Essential Tips for Visiting Manu National Park in Madre de Dios
Travelers to Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, can enjoy a variety of adventure-filled routes, including jungle treks, river cruises, and canopy walks. Guided tours provide insights into the park’s rich biodiversity, with opportunities to observe wildlife such as macaws, tapirs, and monkeys in their natural habitats. To ensure a safe and enjoyable visit, travelers should pack appropriate gear, including sturdy footwear, insect repellent, and camera equipment. Respect for the environment and adherence to park regulations are vital to preserve its ecological integrity. Planning ahead with authorized tour operators guarantees a smooth experience, while eco-friendly practices help minimize human impact. Visiting Manu offers an immersive experience into untouched wilderness, creating unforgettable memories and fostering a deeper appreciation for conservation efforts.
Unique Ecosystems and Habitats within Manu National Park in Madre de Dios
Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, boasts a remarkable array of ecosystems, from dense tropical rainforests to high-altitude grasslands and cloud forests. Each habitat supports distinct communities of plants and animals, making the park a mosaic of ecological zones. The lowland rainforests are teeming with life, hosting countless species of trees, orchids, and medicinal plants, along with diverse fauna like jaguars, giant otters, and poison dart frogs. Mountain forests and puna grasslands provide refuge for species adapted to cooler climates, including spectacled bears and condors. This ecological diversity is essential for maintaining regional and global environmental stability. Protecting these habitats requires ongoing management, scientific research, and community engagement to ensure their resilience against threats such as deforestation and climate change.
Uncovering Hidden Species: Rare and Endemic Animals of Manu National Park
Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, remains a frontier for discovering new and rare species. Its remote and dense forests harbor animals that are yet to be documented, including elusive mammals, colorful birds, and unique insects. Species such as the Andean cock-of-the-rock, giant armadillos, and various endemic frogs thrive in this protected environment. Conservation efforts focus on safeguarding these vulnerable populations from habitat loss and illegal activities. Scientific expeditions continue to reveal the park’s hidden biodiversity, emphasizing its importance as a natural refuge. Protecting these species is vital for understanding ecological dynamics and ensuring the survival of genetic diversity. The park’s role as a natural laboratory underscores the need for ongoing research and habitat preservation.
The Cultural and Indigenous Heritage Linked to Manu National Park in Madre de Dios
Beyond its ecological significance, Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, is intertwined with the cultural heritage of indigenous communities. These groups have inhabited the region for centuries, maintaining traditional practices that harmonize with nature. Their knowledge of medicinal plants, sustainable hunting, and forest management contributes to conservation efforts. Preserving indigenous cultures alongside biodiversity enhances the park’s overall sustainability. Collaborative initiatives aim to empower local communities, ensuring their traditions and livelihoods are protected while promoting environmental stewardship. Recognizing the cultural dimension of Manu enriches understanding and fosters respect for indigenous rights and wisdom, vital for long-term conservation success.
The Role of Manu National Park in Scientific Research and Ecological Understanding
Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, serves as a vital site for ecological and biological research. Its diverse ecosystems provide opportunities to study species interactions, climate adaptation, and evolutionary processes. Researchers have documented thousands of plant and animal species, many of which are endemic or endangered. The park’s relatively undisturbed environment offers insights into natural processes and the impacts of environmental change. Scientific findings from Manu inform global conservation strategies and contribute to our understanding of tropical ecology. Ongoing research supports adaptive management practices, helping to balance human activity with ecological preservation. The park’s role as a natural laboratory underscores its importance for advancing ecological knowledge and promoting sustainable development.
Challenges and Future Threats Facing Manu National Park in Madre de Dios
Despite its protected status, Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, faces ongoing threats such as illegal logging, mining, and deforestation. Climate change also poses risks by altering rainfall patterns and temperature regimes, which can affect habitats and species distributions. Encroachment from agricultural expansion and infrastructure development further jeopardize the park’s integrity. Addressing these challenges requires robust enforcement, community engagement, and international cooperation. Implementing sustainable land-use practices and monitoring environmental changes are essential to mitigate impacts. Ensuring the park’s resilience against future threats is critical for maintaining its ecological and cultural values for generations to come.
Historical and Cultural Heritage of Manu: Ancient Trails and Indigenous Sites
Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, is rich in archaeological and cultural sites that reveal its ancient history. Evidence of past civilizations, including petroglyphs and ceremonial sites, highlights the long-standing relationship between humans and nature in this region. Indigenous communities have preserved traditional knowledge, which is reflected in their sustainable use of forest resources. Protecting these cultural assets alongside biodiversity enhances the park’s value as a heritage site. Educational programs and archaeological research aim to uncover and conserve these historical treasures, fostering a deeper understanding of the region’s cultural significance. Visiting Manu offers a unique opportunity to connect with both natural and cultural history, enriching the experience of explorers and scholars alike.
How Responsible Tourism Supports the Conservation of Manu National Park in Madre de Dios
Promoting responsible tourism in Manu National Park in Madre de Dios, Peru, is essential for sustainable conservation. Visitors can contribute by choosing eco-friendly tour operators, respecting wildlife, and minimizing environmental impact. Education about local ecosystems and cultural heritage fosters appreciation and stewardship among travelers. Supporting community-based initiatives ensures that tourism benefits local populations and encourages conservation efforts. Responsible practices include waste management, avoiding habitat disturbance, and adhering to park guidelines. By engaging in sustainable tourism, visitors help generate funds for conservation projects and local development, ensuring that Manu’s natural and cultural riches are preserved for future generations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes Manu National Park a biodiversity hotspot?
Manu National Park is renowned for its vast and diverse ecosystems, including rainforests, mountain forests, and grasslands. Its varied habitats support a wide range of flora and fauna, including rare and endemic species like jaguars, giant otters, and hundreds of bird species. This ecological richness makes it a critical area for conservation and scientific research.
When was Manu National Park established and why?
Established in 1973, Manu National Park was created to protect its unique ecosystems and biodiversity. Its status as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1987 highlights its global ecological significance. The park’s management focuses on sustainable conservation, involving local communities and international collaborations.
What are the best routes and tips for visiting Manu?
Visitors can enjoy jungle treks, river cruises, and canopy walks. Guided tours provide insights into wildlife like macaws, tapirs, and monkeys. To ensure a safe visit, travelers should bring sturdy footwear, insect repellent, and camera gear. Respect for the environment and planning with authorized operators are essential for a memorable experience.
What ecosystems are found within Manu National Park?
The park features dense tropical rainforests, high-altitude grasslands, and cloud forests. Each habitat hosts distinct species, from jaguars and poison dart frogs in lowlands to spectacled bears and condors in mountain regions. Protecting these ecosystems is vital for regional and global ecological stability.
Are there rare or endemic species in Manu?
Yes, Manu hosts many rare and endemic species, some of which are yet to be fully documented. Animals like the Andean cock-of-the-rock, giant armadillos, and unique frogs thrive here. Scientific expeditions continue to discover new species, emphasizing the park’s importance as a natural refuge.
How do indigenous communities relate to Manu National Park?
Indigenous groups have inhabited the region for centuries, maintaining traditional practices that promote sustainable use of resources. Their knowledge of medicinal plants and forest management contributes to conservation efforts. Collaborations aim to empower these communities while preserving their cultural heritage.
What role does Manu play in scientific research?
The park is a vital site for ecological and biological studies, offering insights into species interactions, climate adaptation, and evolution. Ongoing research helps inform conservation strategies and enhances understanding of tropical ecosystems.
What are the main threats facing Manu today?
Illegal logging, mining, deforestation, and climate change pose significant threats. Encroachment from agriculture and infrastructure development also endangers habitats. Addressing these issues requires enforcement, community engagement, and sustainable land management.
Are there archaeological or cultural sites within Manu?
Yes, the park contains ancient trails, petroglyphs, and indigenous sites that reveal its historical significance. Protecting these cultural assets alongside biodiversity enriches the park’s heritage and offers educational opportunities.
How does responsible tourism support conservation efforts?
Eco-friendly tourism promotes environmental awareness and funds conservation projects. Visitors should choose sustainable operators, respect wildlife, and follow park guidelines. Supporting local communities ensures benefits are shared and ecosystems are preserved.
What are the main conservation milestones achieved in Manu?
Key milestones include its establishment in 1973, recognition as a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1987, and ongoing management practices involving community participation and scientific research. These efforts have helped maintain its ecological integrity over decades.
What should travelers know before visiting Manu?
Preparation is essential: pack appropriate gear, respect local regulations, and plan with authorized guides. Be mindful of environmental impact, and support conservation initiatives during your visit for a responsible tourism experience.
How does climate change threaten Manu’s ecosystems?
Climate change can alter rainfall patterns and temperatures, affecting habitats and species distributions. These changes threaten biodiversity and ecological balance, making conservation efforts more critical than ever.
What future challenges does Manu face?
Future challenges include illegal activities, habitat loss, and climate impacts. Strengthening enforcement, community involvement, and sustainable practices are vital to ensure the park’s resilience and preservation for generations to come.